Updating and Deleting Table Storage Entities with Azure Functions (C# and JavaScript)
Saturday, February 11, 2017
Inserting entities into Table Storage from Azure Functions is a breeze with the Azure Table Storage output bindings. However, the bindings don't directly support updating and deleting entities (yet).
But it's actually pretty easy to support updates and deletes. In C#, this can be done using the Table Storage output binding with a CloudTable parameter. In Node/JavaScript, we can use the azure-storage NPM package.
Our Example
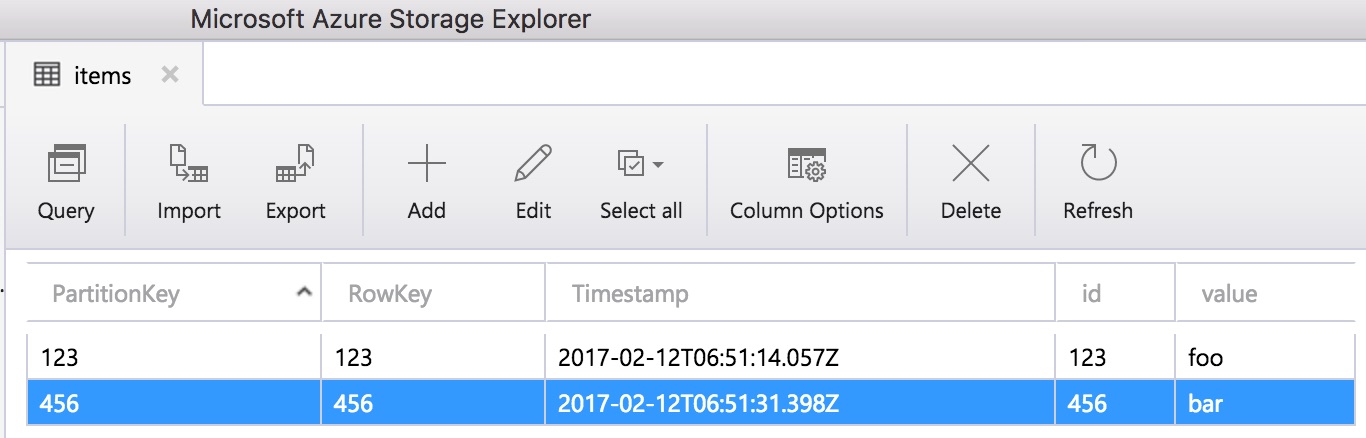
The example we'll be using is fairly straight forward. We'll be updating a table named "items". Each item has an id and a value. We'll use the id as both the partition key and row key for each entity in Table Storage.
C#
Updating an entity
The update function has HTTP trigger and output bindings. It also has a Table Storage output binding that looks exactly like one used to insert entities into a table. Here's the function.json:
{
"bindings": [
{
"authLevel": "anonymous",
"name": "item",
"type": "httpTrigger",
"direction": "in",
"methods": [
"put"
]
},
{
"name": "$return",
"type": "http",
"direction": "out"
},
{
"type": "table",
"name": "outputTable",
"tableName": "items",
"connection": "StorageConnectionString",
"direction": "out"
}
],
"disabled": false
}
But instead of using an ICollector as the outputTable parameter, we'll instead use a CloudTable. This gives us a reference to the table as a CloudTable object from the Table Storage SDK and we have full control over what we can do to the table. Here is the run.csx:
#r "Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage"
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Table;
using System.Net;
public static async Task<HttpResponseMessage> Run(Item item, CloudTable outputTable, TraceWriter log)
{
item.PartitionKey = item.id;
item.RowKey = item.id;
item.ETag = "*";
var operation = TableOperation.Replace(item);
await outputTable.ExecuteAsync(operation);
return new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.NoContent);
}
public class Item: TableEntity
{
public string id { get; set; }
public string value { get; set; }
}
In order to use CloudTable, we need a reference to the Table Storage SDK at the top of the file. All we have to do is create a Replace operation and execute it on the table. By default, the SDK enforces optimistic concurrency via ETags. By setting the ETag to *, we're implementing a "last-write-wins" strategy.
Deleting an entity
Deleting is almost exactly the same...
#r "Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage"
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Table;
using System.Net;
public static async Task<HttpResponseMessage> Run(HttpRequestMessage req, CloudTable outputTable, TraceWriter log)
{
string id = req.GetQueryNameValuePairs()
.First(q => string.Compare(q.Key, "id", true) == 0)
.Value;
var item = new TableEntity(id, id)
{
ETag = "*"
};
var operation = TableOperation.Delete(item);
await outputTable.ExecuteAsync(operation);
return req.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.NoContent);
}
JavaScript
Table Storage Node SDK
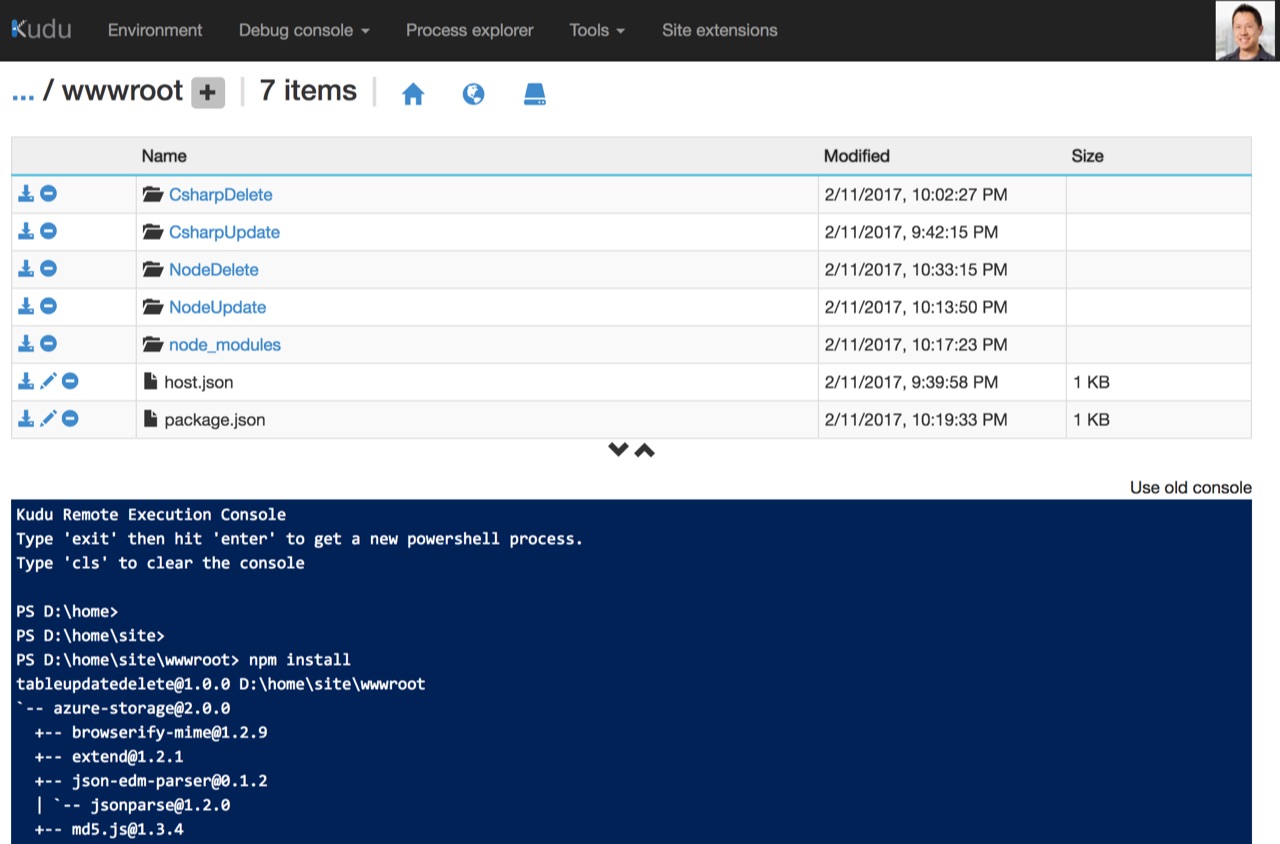
Before we can update and delete entities with JavaScript, we have to install the Azure Table Storage Node SDK to our function app.
We can do this by dropping this package.json file into our function app root (D:\home\site\wwwroot):
{
"name": "tableupdatedelete",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"azure-storage": "^2.0.0"
}
}
Azure Functions currently doesn't run npm install automatically. We need to open up a console in Kudu, navigate to wwwroot, and run npm install to download the SDK. By installing it to the function app root, the packages are available to all JavaScript functions in the app. More details on how to use NPM packages can be found here.
Updating an entity
For our JavaScript update function, we just have the HTTP trigger and output bindings. There's no need for a Table Storage output binding because we won't be using it.
We have our storage account connection in an app setting named StorageConnectionString. We can use this in our function as an environment variable.
let azure = require('azure-storage');
module.exports = function (context, req) {
let item = req.body;
item.PartitionKey = item.id;
item.RowKey = item.id;
let connectionString = process.env.StorageConnectionString;
let tableService = azure.createTableService(connectionString);
tableService.replaceEntity('items', item, (error, result, response) => {
let res = {
statusCode: error ? 400 : 204,
body: null
};
context.done(null, res);
});
};
Like the C# version, the JavaScript code is straight-forward. The JavaScript SDK doesn't enforce optimistic concurrency by default, so there's no need to worry about ETags here.
Deleting an entity
The delete code works just like the update one:
let azure = require('azure-storage');
module.exports = function (context, req) {
let id = req.query.id;
let connectionString = process.env.StorageConnectionString;
let tableService = azure.createTableService(connectionString);
let item = {
PartitionKey: id,
RowKey: id
};
tableService.deleteEntity('items', item, (error, response) => {
let res = {
statusCode: error ? 400 : 204,
body: null
};
context.done(null, res);
});
};
Source Code
The source for the example function app can be found here:
https://github.com/anthonychu/azure-functions-update-delete-table-storage
Inserting entities into Table Storage from Azure Functions is a breeze with the Azure Table Storage output bindings. However, the bindings don't directly support updating and deleting entities (yet).
But it's actually pretty easy to support updates and deletes. In C#, this can be done using the Table Storage output binding with a CloudTable parameter. In Node/JavaScript, we can use the azure-storage NPM package.
Our Example
The example we'll be using is fairly straight forward. We'll be updating a table named "items". Each item has an id and a value. We'll use the id as both the partition key and row key for each entity in Table Storage.

C#
Updating an entity
The update function has HTTP trigger and output bindings. It also has a Table Storage output binding that looks exactly like one used to insert entities into a table. Here's the function.json:
{
"bindings": [
{
"authLevel": "anonymous",
"name": "item",
"type": "httpTrigger",
"direction": "in",
"methods": [
"put"
]
},
{
"name": "$return",
"type": "http",
"direction": "out"
},
{
"type": "table",
"name": "outputTable",
"tableName": "items",
"connection": "StorageConnectionString",
"direction": "out"
}
],
"disabled": false
}
But instead of using an ICollector as the outputTable parameter, we'll instead use a CloudTable. This gives us a reference to the table as a CloudTable object from the Table Storage SDK and we have full control over what we can do to the table. Here is the run.csx:
#r "Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage"
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Table;
using System.Net;
public static async Task<HttpResponseMessage> Run(Item item, CloudTable outputTable, TraceWriter log)
{
item.PartitionKey = item.id;
item.RowKey = item.id;
item.ETag = "*";
var operation = TableOperation.Replace(item);
await outputTable.ExecuteAsync(operation);
return new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.NoContent);
}
public class Item: TableEntity
{
public string id { get; set; }
public string value { get; set; }
}
In order to use CloudTable, we need a reference to the Table Storage SDK at the top of the file. All we have to do is create a Replace operation and execute it on the table. By default, the SDK enforces optimistic concurrency via ETags. By setting the ETag to *, we're implementing a "last-write-wins" strategy.
Deleting an entity
Deleting is almost exactly the same...
#r "Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage"
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Table;
using System.Net;
public static async Task<HttpResponseMessage> Run(HttpRequestMessage req, CloudTable outputTable, TraceWriter log)
{
string id = req.GetQueryNameValuePairs()
.First(q => string.Compare(q.Key, "id", true) == 0)
.Value;
var item = new TableEntity(id, id)
{
ETag = "*"
};
var operation = TableOperation.Delete(item);
await outputTable.ExecuteAsync(operation);
return req.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.NoContent);
}
JavaScript
Table Storage Node SDK
Before we can update and delete entities with JavaScript, we have to install the Azure Table Storage Node SDK to our function app.
We can do this by dropping this package.json file into our function app root (D:\home\site\wwwroot):
{
"name": "tableupdatedelete",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"azure-storage": "^2.0.0"
}
}
Azure Functions currently doesn't run npm install automatically. We need to open up a console in Kudu, navigate to wwwroot, and run npm install to download the SDK. By installing it to the function app root, the packages are available to all JavaScript functions in the app. More details on how to use NPM packages can be found here.

Updating an entity
For our JavaScript update function, we just have the HTTP trigger and output bindings. There's no need for a Table Storage output binding because we won't be using it.
We have our storage account connection in an app setting named StorageConnectionString. We can use this in our function as an environment variable.
let azure = require('azure-storage');
module.exports = function (context, req) {
let item = req.body;
item.PartitionKey = item.id;
item.RowKey = item.id;
let connectionString = process.env.StorageConnectionString;
let tableService = azure.createTableService(connectionString);
tableService.replaceEntity('items', item, (error, result, response) => {
let res = {
statusCode: error ? 400 : 204,
body: null
};
context.done(null, res);
});
};
Like the C# version, the JavaScript code is straight-forward. The JavaScript SDK doesn't enforce optimistic concurrency by default, so there's no need to worry about ETags here.
Deleting an entity
The delete code works just like the update one:
let azure = require('azure-storage');
module.exports = function (context, req) {
let id = req.query.id;
let connectionString = process.env.StorageConnectionString;
let tableService = azure.createTableService(connectionString);
let item = {
PartitionKey: id,
RowKey: id
};
tableService.deleteEntity('items', item, (error, response) => {
let res = {
statusCode: error ? 400 : 204,
body: null
};
context.done(null, res);
});
};
Source Code
The source for the example function app can be found here: https://github.com/anthonychu/azure-functions-update-delete-table-storage
